

Its moment of inertia about an axis perpendicular to its plane and passing through a point on its rim will be.īasically, for any rotating object, the moment of inertia can be calculated by taking the distance of each particle from the axis of rotation (r in the equation), squaring that value (that's the r 2 term), and multiplying it times the mass of that particle.

Because r is the distance to the axis of rotation from each piece of mass that makes up the object, the moment of inertia for any object depends on the chosen axis. for all the point masses that make up the object. Since we have a compound object in both cases, we can use the parallel-axis theorem to find the moment of inertia about each axis. (In order to simplify the calculation we have assumed that the mass m is a point at the end of the lever arm r and the rod it is attached to is massless.
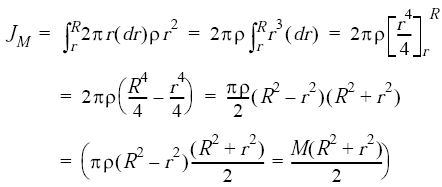
The radius of the sphere is 20.0 cm and has mass 1.0 kg. The moment of inertia of a collection of masses is given by: I miri 2(7.3) If there is only one mass (as shown in Fig. The rod has length 0.5 m and mass 2.0 kg. Moment of inertia of a uniform circular disc about a diameter is `I`. We defined the moment of inertia I of an object to be. Find the moment of inertia of the rod and solid sphere combination about the two axes as shown below. Subsequently, one may also ask, what is the moment of inertia of a uniform circular disk? The polar moment of inertia, also known as second polar moment of area, is a quantity used to describe resistance to torsional deformation (deflection), in cylindrical objects (or segments of cylindrical object) with an invariant cross-section and no significant warping or out-of-plane deformation.īeside above, what does radius of gyration mean? Radius of gyration or gyradius of a body about an axis of rotation is defined as the radial distance of a point, from the axis of rotation at which, if whole mass of the body is assumed to be concentrated, its moment of inertia about the given axis would be the same as with its actual distribution of mass. In such cases, an axis passing through the centroid of the shape is probably implied. Often though, one may use the term 'moment of inertia of circle', missing to specify an axis.

Likewise, people ask, what is polar moment of inertia of circle? The second moment of area (moment of inertia) is meaningful only when an axis of rotation is defined. This equation is equivalent to I = π D 2 / 64 when we express it taking the diameter (D) of the circle. Here, r is the radius and the axis is passing through the centre. Moment of inertia of a circle or the second- moment area of a circle is usually determined using the following expression I = π R 4 / 4. Īlso note that unlike the second moment of area, the product of inertia may take negative values.What is the moment of inertia of a circle? What is the moment of inertia of a circle? Principal axes Reference Table Area Moments of Inertia


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
